Looking for a way to enhance your skills and join the workforce? Look no further than AICTE's Kaushal Augmentation and Restructuring Mission of AICTE (KARMA) scheme!
The AICTE has introduced this initiative to certify and provide skill training to students studying in AICTE-approved institutions, CFTIs, nearby schools, and even to those who dropped out of school after the 10th grade and are seeking employment opportunities.
As per the current industry requirements, the KARMA scheme offers planned skill initiatives to create a skilled and certified workforce
Did you know that India has a huge population of young people, with 25.9% under the age of 14 and 66% in the working-age group of 15-59? However, the country is experiencing a qualified worker shortage despite this number. With only 2% having formal vocational training and 6.1% receiving non-formal training. That's a big problem!
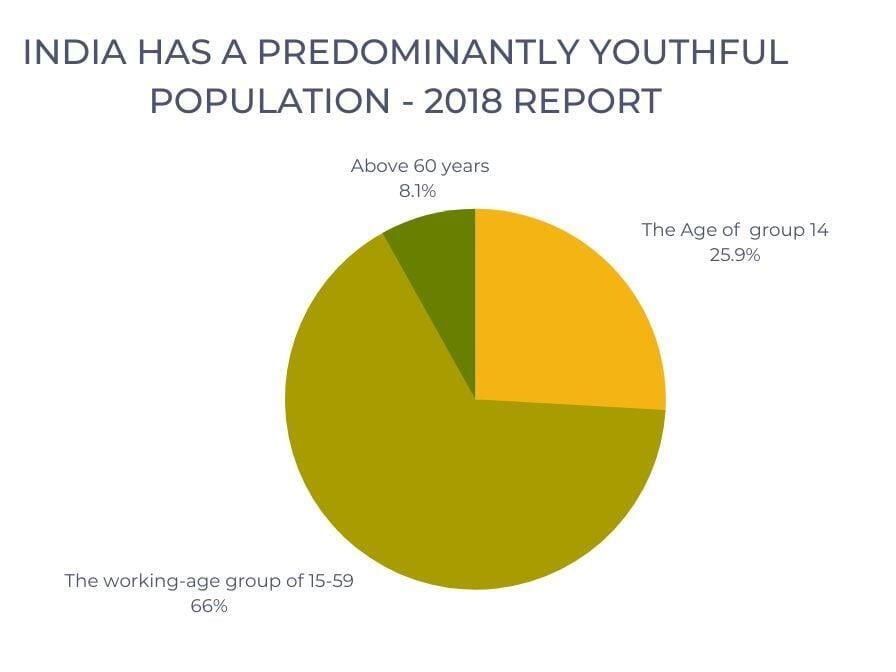
India’s young population (25.9% below 14 and 66% working age) is a demographic dividend. However, job skills present a challenge as only 2% have received formal vocational training.
But don't worry; vocational education can be a game-changer for India's economic growth. That's why the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 requires all educational institutions to integrate vocational education into their offerings, and the All-India Council for Technical Education (AICTE) is launching the "Kaushal Augmentation and Restructuring Mission of AICTE" (AICTE-Approved KARMA SCHEME) to help learners.
So, if you want to be part of India's success story, get yourself some vocational training and join the skilled workforce of the future!
LET'S GET INTO DETAILS OF THE KARMA SCHEME
LET'S GET INTO DETAILS OF THE KARMA SCHEME
AN INTRODUCTION TO THE AICTE-APPROVED KARMA SCHEME
The AICTE scheme KARMA, launched on December 15, 2021, aims to enhance the skills of the community using the infrastructure of approved institutions, including 3.5K polytechnics and 3K engineering colleges. This KARMA scheme offers NSQF-aligned, short-duration, domain-specific courses in a self-financing mode with assessments.
- AICTE launched the KARMA scheme to enhance community skills using the existing infrastructure of AICTE-approved institutions.
- Admission is open to anyone who passed the 10th class, with priority given to local learners.
- Institutes can admit up to 50% of the approved intake, with 5% of seats reserved for PwD students under the fee waiver scheme.
- Training can be fully in-person or through a blended approach under the KARMA scheme of training.
- The program will offer courses that align with the vocational trades specified in the SAMAGRA SIKSHA vocational scheme or other short-duration courses that follow the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- The program was implemented through a self-funded approach, which required educational institutions to bear the training costs.
- Institutes may offer fee-based courses in higher-level skills and courses that are NSQF level 5 and above.
UNDERSTANDING THE GOALS OF THE AICTE - APPROVED KARMA SCHEME
The KARMA scheme is designed to create a skilled and certified workforce that will not only help India's growth but also make it the global skills capital.
Here's what the KARMA scheme aims to do:
- To create a certified and skilled workforce, skill initiatives are being planned in a calculated manner.
- Encourage institutions to use their infrastructure for skill training during off-hours by setting up existing infrastructure for skill courses.
The KARMA scheme allows individuals to receive training in skills that are specifically in demand in various fields, particularly in core engineering sectors. The training aims to lead to employment or self-employment opportunities.
An independent third-party agency will assess and certify your training, allowing you to get formal certification for your informal skills or transition to formal sector jobs.
Even technical institutes can offer training in non-technical courses with job or self-employment opportunities in the local area.
REQUIREMENTS AND REGULATIONS FOR ENROLLMENT IN THE AICTE-APPROVED KARMA SCHEME
- THE CRITERIA AND ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS FOR STUDENTS.
- The KARMA scheme is open to school dropouts who want to attain higher-order skills and proximity to a college or polytechnic.
- Applicants must have passed at least the 10th standard/ITIs and meet NSQF-defined criteria for the job role.
- Any 10th class and above may join, with preference given to local learners.
- Institutes can admit 50% of the approved intake of AICTE in relevant branches.
- 5% of seats are reserved for PwD students under the fee waiver scheme.
- There is no age limit for admission under the KARMA scheme.
- PARTICIPATION CRITERIA AND RULES FOR TRAINING INSTITUTIONS.
- AICTE’s KARMA scheme is open to all AICTE-approved institutions, with a priority on those offering technical courses.
- Selected institutions must comply with scheme norms set by the government for successful implementation.
- AICTE-approved technical institutes and polytechnics can apply online through a public notice on the AICTE website.
- Proposals must be submitted in the prescribed format and evaluated based on merit by AICTE.
- The list of selected institutions and programs will be announced on the AICTE website and through registered email.
AICTE-APPROVED KARMA SCHEME PARTICIPATION GUIDELINES
The KARMA scheme is a government initiative that provides vocational training to school dropouts and candidates who have passed at least the 10th standard, or ITIs, among others. The scheme aims to develop higher-order skills relevant to future job and entrepreneurial opportunities.
Here are the guidelines for the KARMA scheme, showing key information about the implementation of a skill development scheme.
1. Eligibility
- All AICTE-approved institutions running relevant technical courses can take part.
- Institutions must follow the norms specified in the KARMA scheme and those decided by the government from time to time.
2. Selection Procedure
- AICTE will invite online applications from AICTE-approved technical institutes and polytechnics.
- The assessment of proposals will be based on their merit.
- The AICTE will announce the list of approved institutions and programs on its website and send it through registered mail.
3. Target Beneficiaries
- This program is beneficial for individuals who live near a college or polytechnic institution, have dropped out of school after completing the 10th grade, and wish to get advanced skills.
- The eligibility criteria include passing at least the 10th standard/ITIs and fulfilling other requirements for the specific job role, as defined by the NSQF.
- An Aadhaar card is mandatory for enrollment in the program.
4. Admission
- Any 10th-class pass out and above can join such programs.
- Priority will be given to students residing within the local community.
- Educational institutions are permitted to admit 50% of the approved AICTE intake in the relevant branch.
- Each institute must reserve 5% of its seats for students with disabilities under the Fee Waiver Scheme.
- There is no age bar for admission under the KARMA scheme, and admission may be done throughout the year.
5. Modes of Training
- Training can be 100% contact-based or blended.
- The theory part of the course may be delivered in digital/online mode, and the practical training will be delivered at the institute’s training center.
6. The Job Roles and Qualifications
- Colleges and polytechnics are planning to provide programs that are divided into smaller, credit-based modules. These modules will be focused on job and entrepreneurship opportunities that are relevant to the specific group of students.
- NASSCOM is planning to upload the qualifications for courses like 3D Printing, AI & Robotics, Architectural Drafting, and Basic 3D Design onto the National Qualifications Register in the near future.
7. Self-Financing Mode
- The KARMA scheme will be implemented in a self-financing mode.
- The institute itself will manage all the expenses related to the training.
- Approved institutions and training providers may offer fee-based training programs for popular courses that have high demand in the industry and offer above-average wages.
8. Credit Framework
- Banking of credits for skill shall be permitted to enable the mobility of learners as per progressive job roles in the skill vertical and further towards higher studies.
- The credit system for these courses will be in line with the guidelines provided by the National Higher Education Qualifications Framework (NHEQF) and will be in coordination with the National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
9. Infrastructure
- Each institution must have appropriate laboratory/workshop facilities to conduct face-to-face skills training and practical sessions.
- The institution can either own these facilities or arrange them through partnerships with industrial partners, social organizations that provide skills training, NCVET/AICTE-approved training providers, or any other training partner with the required infrastructure in the relevant sector.
10. Faculty/Trainers
- The faculty members for the program will include the current institution staff as well as a group of guest/visiting/adjunct faculty, who will be sourced from either the industry or NCVET-approved training partners.
11. Technical Qualifications and National Occupational Standards (NOS)
- Institutes can select technical qualifications and NOS from the National Qualification Register for STT.
- National Qualification Register link: https://www.nqr.gov.in
THE SKILL DEVELOPMENT MODEL FOR THE AICTE-APPROVED KARMA SCHEME
AICTE HAS SUGGESTED THREE DIFFERENT WAYS TO TEACH SKILLS TO STUDENTS IN INDIA.
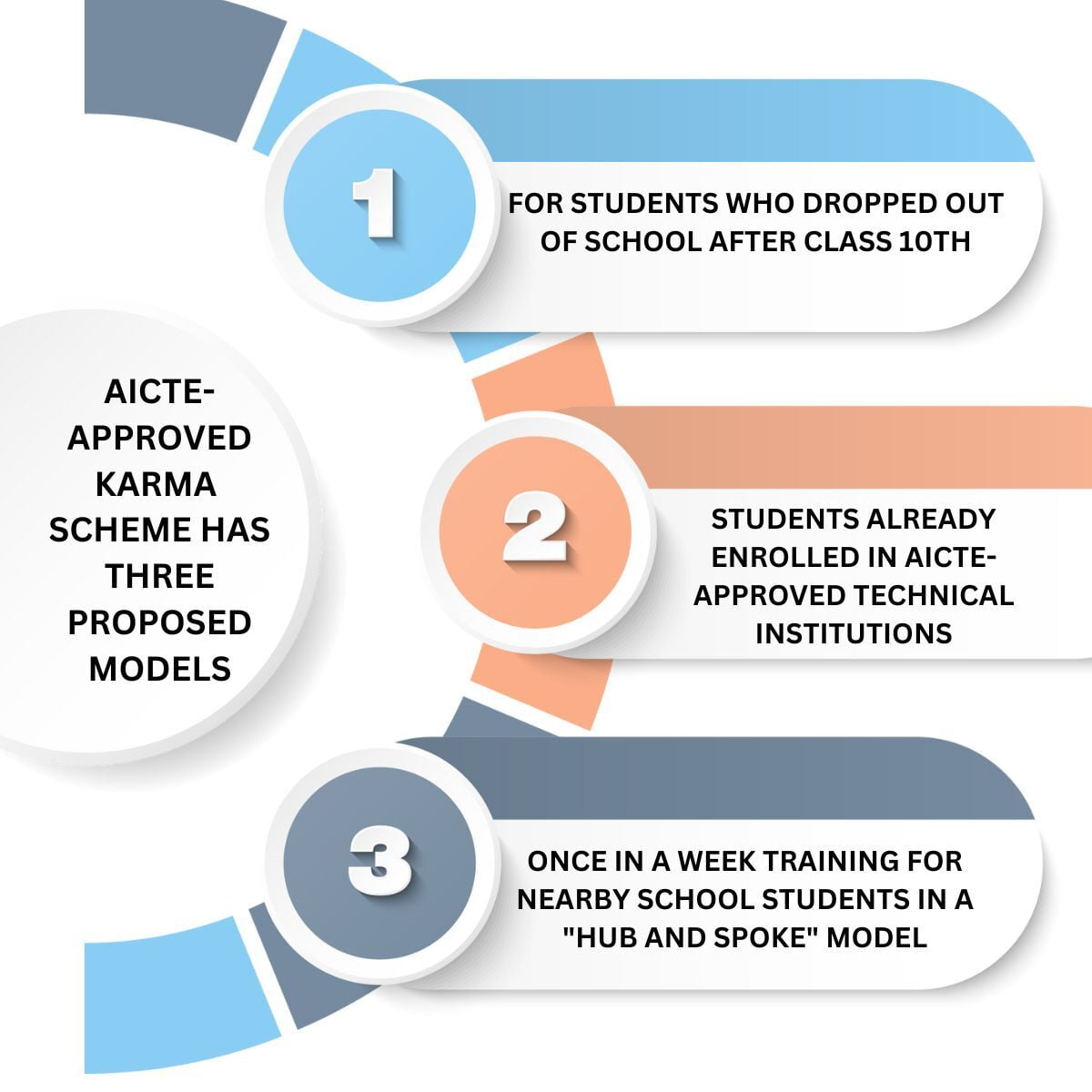
The three models proposed by the KARMA scheme aim to provide skill training to 10th-class dropouts, technical students, and school students. This will help them to become industry-ready, learn new skills, and build their careers
I. Model 1→For students who dropped out of school after the 10th class. They can get training to learn new skills and get a job.
II. Model 2→ For students who are already studying at AICTE-approved technical institutions. They will be given advanced skill training during the 4th to 7th semesters to make them ready for the industry.
III. Model 3→Connecting school-based education with higher education. AICTE suggests starting skill-based training once a week for nearby school students in a "Hub and Spoke" Model. The training will be given by HEIs without any financial burden on the students. Institutions can contact nearby schools and bring their students to their campus for a day of skill-based training until a specified skill set is achieved.
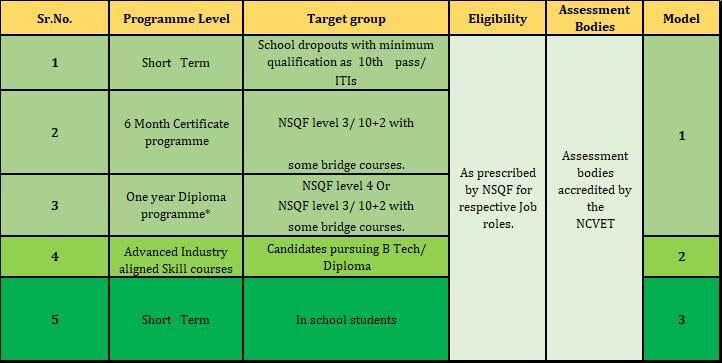
The students will receive certificates based on occupational hours and NSQF levels approved by NCVET. This will encourage students to build long-term careers through higher education. The schools and HEIs will have a better connection and increase admissions in technical courses.
So, what are you waiting for? Get skilled, get certified, and get ahead with KARMA!
FAQs
FAQs
1. What is the KARMA scheme?
» The KARMA scheme is a government initiative to enhance community skills using the existing infrastructure of AICTE-approved institutions.
2. Who can apply for the KARMA scheme?
»The scheme is open to anyone who has passed 10th grade, with priority given to local learners.
3. What kind of courses are offered under the KARMA scheme?
»NSQF-aligned short-duration domain-specific courses are offered based on vocational trades prescribed in Samagra Siksha vocational scheme.
4. Can institutes offer fee-based courses under the KARMA scheme?
»Yes, institutes may offer fee-based courses in higher-level skills and NSQF level 5 and above courses.
5. Who is eligible to participate in the KARMA scheme?
» All AICTE-approved institutions running relevant technical courses can participate.
6. How are proposals evaluated for the KARMA scheme?
»Proposals are evaluated based on merit by AICTE.
7. What are the eligibility requirements for students under the KARMA scheme?
» Applicants must have passed at least 10th standard/ITIs and meet NSQF-defined criteria for the job role.
8. Can school dropouts apply for the KARMA scheme?
»Yes, school dropouts can apply for the scheme to attain higher-order skills.
9. Is there any age limit for admission under the KARMA scheme?
»No, there is no age limit for admission under this scheme.
10. How are the training expenses managed under the KARMA scheme?
» The scheme is implemented in self-financing mode, with training expenses managed by institutes.
11. What is the objective of the KARMA scheme?
» The scheme aims to create a skilled and certified workforce that will help India’s growth and to make it the global skills capital.
12. How can institutes participate in the KARMA scheme?
»AICTE-approved Technical Institutes/Polytechnics can apply online through a Public Notice on the AICTE website.
13. What are the modes of training offered under the KARMA scheme?
»Training can be fully in-person or through a blended approach.
14. Is possession of an Aadhaar card necessary to participate in the KARMA scheme?
»Yes, possession of an Aadhaar card is necessary.
15. What is the fee waiver scheme under the KARMA scheme?
» 5% of seats are reserved for PwD students under the fee waiver scheme.
